Device Plugin 相关流程分析
讲解DevicePlugin相关的全部流程
Device Plugin 相关流程分析
主要参考文档:
目标版本:deviceplugin/v1alpha
总体机制
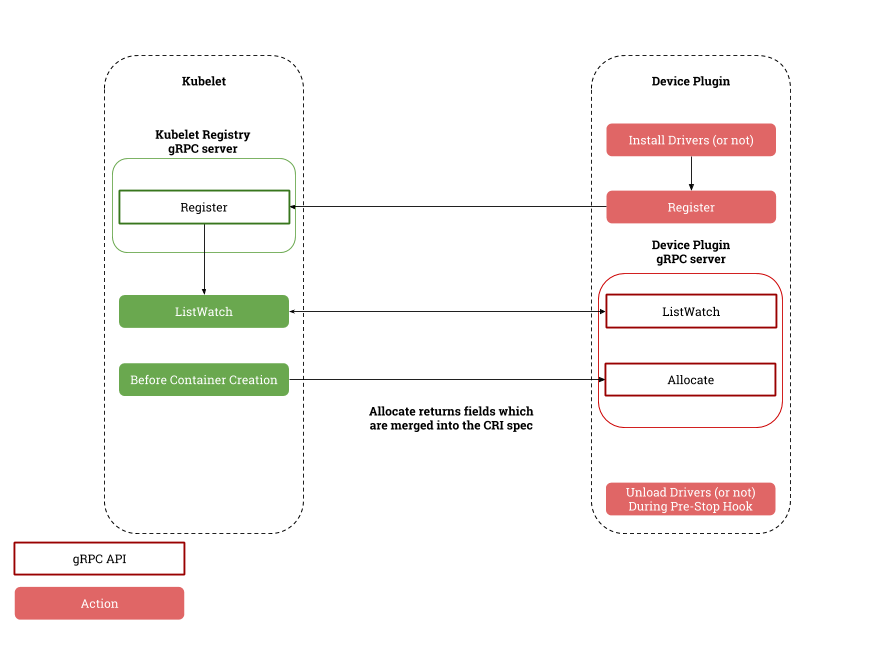
总的来说,插件需要先注册到Kubelet;kubelet会进行监听,当插件的状态发生变化,或是消失时,会返回新的状态,进行更新;当kubelet需要资源时,会通过Allocate向DevicePlugin进行申请。
DevicePlugin端
想要实现一个DevicePlugin,需要实现DevicePlugin、Registration接口,该接口中包含如下内容:
// DevicePlugin is the service advertised by Device Plugins
service DevicePlugin {
rpc ListAndWatch(Empty) returns (stream ListAndWatchResponse) {}
rpc Allocate(AllocateRequest) returns (AllocateResponse) {}
}
// Registration is the service advertised by the Kubelet
service Registration {
rpc Register(RegisterRequest) returns (Empty) {}
}
实现Registration时,DevicePlugin作为客户端。
实现DevicePlugin时,DevicePlugin作为服务端。
与DevicePlugin交互的对象始终是kubelet。
Registration
// Registration is the service advertised by the Kubelet
service Registration {
rpc Register(RegisterRequest) returns (Empty) {}
}
Registration接口描述了DevicePlugin向kubelet注册自己的行为。
message RegisterRequest {
string version = 1;
string endpoint = 2;
string resource_name = 3;
}
在进行注册时,DevicePlugin需要向Kubelet发送:
endpoint:unix socket的名称version:版本信息resource_name:资源的名称
成功注册后,DevicePlugin应当开启grpc服务
(ASK)在注册时,通过已经定义好的grpc接口进行通信,错误信息如何返回?
(ASNWER)请看下面关于
ManagerImpl.Register的分析,会返回一个error
DevicePlugin (v1alpha)
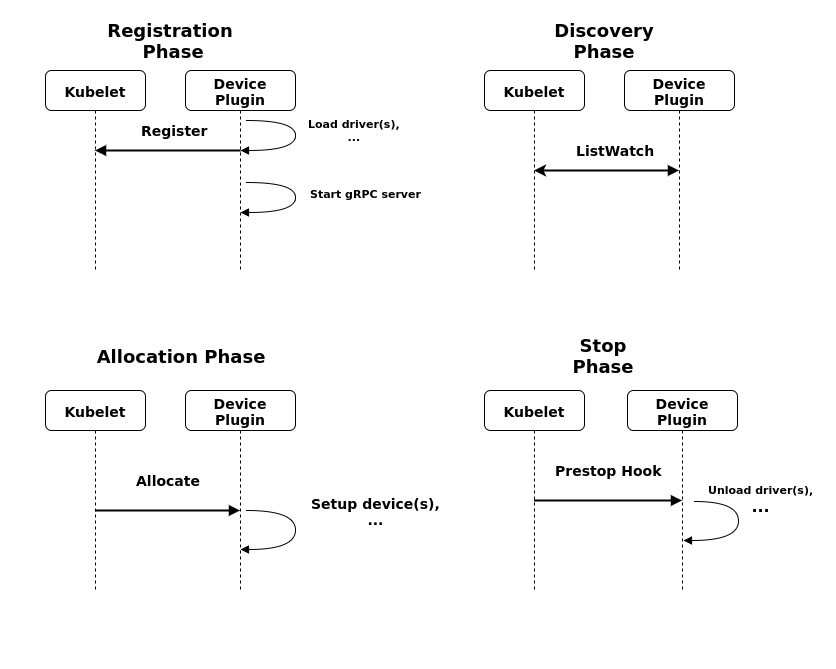
ListAndWatch
rpc ListAndWatch(Empty) returns (stream ListAndWatchResponse) {}
message ListAndWatchResponse {
repeated Device devices = 1; // 设备列表
}
message Device {
string ID = 1; // 设备ID
string health = 2; // 设备是否健康
}
当某个Device的状态发生变化或是消失时,ListAndWatch会返回一个设备列表devices。
Allocate
rpc Allocate(AllocateRequest) returns (AllocateResponse) {}
message AllocateRequest {
repeated string devicesIDs = 1;
}
message AllocateResponse {
map<string, string> envs = 1; // 需要设置的环境变量
repeated Mount mounts = 2; // 容器的挂载信息
repeated DeviceSpec devices = 3; // 容器的设备信息
map<string, string> annotations = 4;// 需要加入到容器运行时的annotations(注解)
}
// 要挂载到容器中的设备
message Mount {
string container_path = 1; // 容器中挂载的路径
string host_path = 2; // 主机中的安装路径
bool read_only = 3; // 挂载的设备是否可读
}
// 要安装到容器中的设备
message DeviceSpec {
string container_path = 1; // 容器中挂载的路径
string host_path = 2; // 主机中的安装路径
// Cgroups 权限
// r - 允许容器读取
// w - 允许容器创建
// m - 允许容器创建尚不存在的文件
string permissions = 3;
}
当需要申请资源时,Kubelet会通过Allocate接口向DevicePlugin申请资源,该接口可以同时为多个容器申请资源(devicesIDs)。
返回的信息在上方已经进行了说明。
(ASK)如何对CPU资源进行挂载?
(ANSWER)更改对docker的cpu资源的分配,来达到与挂载相似的效果?
(ASK)挂载等操作由
Kubelet完成还是由DevicePlugin完成?
Kubelet端
本部分代码阅读顺序以及分析思路来自于参考文档2
// Manager manages all the Device Plugins running on a node.
type Manager interface {
Start(activePods ActivePodsFunc, sourcesReady config.SourcesReady) error
Allocate(pod *v1.Pod, container *v1.Container) error
UpdatePluginResources(node *schedulerframework.NodeInfo, attrs *lifecycle.PodAdmitAttributes) error
Stop() error
GetDeviceRunContainerOptions(pod *v1.Pod, container *v1.Container) (*DeviceRunContainerOptions, error)
GetCapacity() (v1.ResourceList, v1.ResourceList, []string)
GetWatcherHandler() cache.PluginHandler
GetDevices(podUID, containerName string) ResourceDeviceInstances
GetAllocatableDevices() ResourceDeviceInstances
ShouldResetExtendedResourceCapacity() bool
GetTopologyHints(pod *v1.Pod, container *v1.Container) map[string][]topologymanager.TopologyHint
GetPodTopologyHints(pod *v1.Pod) map[string][]topologymanager.TopologyHint
UpdateAllocatedDevices()
}
Start
// Start starts the Device Plugin Manager and start initialization of
// podDevices and allocatedDevices information from checkpointed state and
// starts device plugin registration service.
func (m *ManagerImpl) Start(activePods ActivePodsFunc, sourcesReady config.SourcesReady) error {
klog.V(2).Infof("Starting Device Plugin manager")
m.activePods = activePods
m.sourcesReady = sourcesReady
// Loads in allocatedDevices information from disk.
err := m.readCheckpoint()
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("Continue after failing to read checkpoint file. Device allocation info may NOT be up-to-date. Err: %v", err)
}
socketPath := filepath.Join(m.socketdir, m.socketname)
if err = os.MkdirAll(m.socketdir, 0750); err != nil {
return err
}
if selinux.SELinuxEnabled() {
if err := selinux.SetFileLabel(m.socketdir, config.KubeletPluginsDirSELinuxLabel); err != nil {
klog.Warningf("Unprivileged containerized plugins might not work. Could not set selinux context on %s: %v", m.socketdir, err)
}
}
// Removes all stale sockets in m.socketdir. Device plugins can monitor
// this and use it as a signal to re-register with the new Kubelet.
if err := m.removeContents(m.socketdir); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Fail to clean up stale contents under %s: %v", m.socketdir, err)
}
s, err := net.Listen("unix", socketPath)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf(errListenSocket+" %v", err)
return err
}
m.wg.Add(1)
m.server = grpc.NewServer([]grpc.ServerOption{}...)
pluginapi.RegisterRegistrationServer(m.server, m)
go func() {
defer m.wg.Done()
m.server.Serve(s)
}()
klog.V(2).Infof("Serving device plugin registration server on %q", socketPath)
return nil
}
总体来说,Start函数,顺序执行了以下几步关键操作:
- 创建socket目录,删除该目录下的所有文件后,监听socket文件
- 创建
grpc server(m.server),将RegistrationServer注册到m.server并开启服务(协程)
到此,注册服务已经开启(也就是DevicePlugin在注册时需要调用的服务),当DevicePlugin进行注册时,就会调用m.Register函数进行注册。
Register
// Register registers a device plugin.
func (m *ManagerImpl) Register(ctx context.Context, r *pluginapi.RegisterRequest) (*pluginapi.Empty, error) {
klog.Infof("Got registration request from device plugin with resource name %q", r.ResourceName)
metrics.DevicePluginRegistrationCount.WithLabelValues(r.ResourceName).Inc()
var versionCompatible bool
for _, v := range pluginapi.SupportedVersions {
if r.Version == v {
versionCompatible = true
break
}
}
if !versionCompatible {
errorString := fmt.Sprintf(errUnsupportedVersion, r.Version, pluginapi.SupportedVersions)
klog.Infof("Bad registration request from device plugin with resource name %q: %s", r.ResourceName, errorString)
return &pluginapi.Empty{}, fmt.Errorf(errorString)
}
if !v1helper.IsExtendedResourceName(v1.ResourceName(r.ResourceName)) {
errorString := fmt.Sprintf(errInvalidResourceName, r.ResourceName)
klog.Infof("Bad registration request from device plugin: %s", errorString)
return &pluginapi.Empty{}, fmt.Errorf(errorString)
}
// TODO: for now, always accepts newest device plugin. Later may consider to
// add some policies here, e.g., verify whether an old device plugin with the
// same resource name is still alive to determine whether we want to accept
// the new registration.
go m.addEndpoint(r)
return &pluginapi.Empty{}, nil
}
Register函数经过了以下主要过程:
- 检测插件版本是否兼容, 不兼容时返回错误
- 检测插件名称是否合法,不合法时返回错误
- 开启协程,添加
EndPoint,并且返回Empty
addEndPoint
func (m *ManagerImpl) addEndpoint(r *pluginapi.RegisterRequest) {
new, err := newEndpointImpl(filepath.Join(m.socketdir, r.Endpoint), r.ResourceName, m.callback)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Failed to dial device plugin with request %v: %v", r, err)
return
}
m.registerEndpoint(r.ResourceName, r.Options, new)
go func() {
m.runEndpoint(r.ResourceName, new)
}()
}
newEndpointImpl
// newEndpointImpl creates a new endpoint for the given resourceName.
// This is to be used during normal device plugin registration.
func newEndpointImpl(socketPath, resourceName string, callback monitorCallback) (*endpointImpl, error) {
client, c, err := dial(socketPath)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Can't create new endpoint with path %s err %v", socketPath, err)
return nil, err
}
return &endpointImpl{
client: client,
clientConn: c,
socketPath: socketPath,
resourceName: resourceName,
cb: callback,
}, nil
}
// dial establishes the gRPC communication with the registered device plugin. https://godoc.org/google.golang.org/grpc#Dial
func dial(unixSocketPath string) (pluginapi.DevicePluginClient, *grpc.ClientConn, error) {
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 10*time.Second)
defer cancel()
c, err := grpc.DialContext(ctx, unixSocketPath, grpc.WithInsecure(), grpc.WithBlock(),
grpc.WithContextDialer(func(ctx context.Context, addr string) (net.Conn, error) {
return (&net.Dialer{}).DialContext(ctx, "unix", addr)
}),
)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, fmt.Errorf(errFailedToDialDevicePlugin+" %v", err)
}
return pluginapi.NewDevicePluginClient(c), c, nil
}
type endpointImpl struct {
client pluginapi.DevicePluginClient
clientConn *grpc.ClientConn
socketPath string
resourceName string
stopTime time.Time
mutex sync.Mutex
cb monitorCallback
}
newEndpointImpl会接受资源对应的socketPath以及resourceName,调用dial函数与注册的资源建立grpc链接。
在完成连接后,newEndpointImpl会返回一个已经与目标建立了链接的client。
registerEndpoint
func (m *ManagerImpl) registerEndpoint(resourceName string, options *pluginapi.DevicePluginOptions, e endpoint) {
m.mutex.Lock()
defer m.mutex.Unlock()
m.endpoints[resourceName] = endpointInfo{e: e, opts: options}
klog.V(2).Infof("Registered endpoint %v", e)
}
这步操作非常简单,就是将resourceName及其对应的endpoint进行注册到了ManagerImpl中的endpointsmap中。
对ManagerImpl.endpoints信息的访问操作是互斥的。
runEndpoint
func (m *ManagerImpl) runEndpoint(resourceName string, e endpoint) {
e.run()
e.stop()
m.mutex.Lock()
defer m.mutex.Unlock()
if old, ok := m.endpoints[resourceName]; ok && old.e == e {
m.markResourceUnhealthy(resourceName)
}
klog.V(2).Infof("Endpoint (%s, %v) became unhealthy", resourceName, e)
}
func (e *endpointImpl) run() {
stream, err := e.client.ListAndWatch(context.Background(), &pluginapi.Empty{})
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf(errListAndWatch, e.resourceName, err)
return
}
for {
response, err := stream.Recv()
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf(errListAndWatch, e.resourceName, err)
return
}
devs := response.Devices
klog.V(2).Infof("State pushed for device plugin %s", e.resourceName)
var newDevs []pluginapi.Device
for _, d := range devs {
newDevs = append(newDevs, *d)
}
e.callback(e.resourceName, newDevs)
}
}
// 默认的callback
func (m *ManagerImpl) genericDeviceUpdateCallback(resourceName string, devices []pluginapi.Device) {
m.mutex.Lock()
m.healthyDevices[resourceName] = sets.NewString()
m.unhealthyDevices[resourceName] = sets.NewString()
m.allDevices[resourceName] = make(map[string]pluginapi.Device)
for _, dev := range devices {
m.allDevices[resourceName][dev.ID] = dev
if dev.Health == pluginapi.Healthy {
m.healthyDevices[resourceName].Insert(dev.ID)
} else {
m.unhealthyDevices[resourceName].Insert(dev.ID)
}
}
m.mutex.Unlock()
if err := m.writeCheckpoint(); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("writing checkpoint encountered %v", err)
}
}
这一步非常重要,这一步用于运行endpoint,会调用endpoint.run()方法。
endpoint.run()方法会调用ListAndWatch方法并循环等待DevicePlugin发过来的stream数据,当且仅当DevicePlugin发送数据错误时退出;当接收到正常的数据时会调用在endpoint中定义好的回调方法e.callback,该回调方法会经过一长串调用链,最终调用ManagerImpl.genericDeviceUpdateCallback方法(可以修改执行的回调函数),genericDeviceUpdateCallback方法会使用新的devices列表信息更新m.allDevices。
当异常退出时,会返回runEndpoint方法中继续执行,由创建者完成对资源的UnHealthy标记。
(ASK)DevicePlugin什么时候发送数据错误?
GetCapacity
需要注意的是,GetCapacity并不是在protobuf中定义的方法,而是在ManagerImpl中定义的。
GetCapacity() (v1.ResourceList, v1.ResourceList, []string)
// ResourceList is a set of (resource name, quantity) pairs.
type ResourceList map[ResourceName]resource.Quantity
type ResourceName string
type Quantity struct {
// i is the quantity in int64 scaled form, if d.Dec == nil
i int64Amount
// d is the quantity in inf.Dec form if d.Dec != nil
d infDecAmount
// s is the generated value of this quantity to avoid recalculation
s string
// Change Format at will. See the comment for Canonicalize for
// more details.
Format
}
这里Quantity的结构有点深,我没有仔细看,据说:
资源列表是一个map,key是资源名,value是资源量,资源量是可以采用多种方式表达的
接下来看GetCapacity函数:
func (m *ManagerImpl) GetCapacity() (v1.ResourceList, v1.ResourceList, []string) {
needsUpdateCheckpoint := false
var capacity = v1.ResourceList{}
var allocatable = v1.ResourceList{}
deletedResources := sets.NewString()
m.mutex.Lock()
for resourceName, devices := range m.healthyDevices {
eI, ok := m.endpoints[resourceName]
if (ok && eI.e.stopGracePeriodExpired()) || !ok {
// The resources contained in endpoints and (un)healthyDevices
// should always be consistent. Otherwise, we run with the risk
// of failing to garbage collect non-existing resources or devices.
if !ok {
klog.Errorf("unexpected: healthyDevices and endpoints are out of sync")
}
delete(m.endpoints, resourceName)
delete(m.healthyDevices, resourceName)
deletedResources.Insert(resourceName)
needsUpdateCheckpoint = true
} else {
capacity[v1.ResourceName(resourceName)] = *resource.NewQuantity(int64(devices.Len()), resource.DecimalSI)
allocatable[v1.ResourceName(resourceName)] = *resource.NewQuantity(int64(devices.Len()), resource.DecimalSI)
}
}
for resourceName, devices := range m.unhealthyDevices {
eI, ok := m.endpoints[resourceName]
if (ok && eI.e.stopGracePeriodExpired()) || !ok {
if !ok {
klog.Errorf("unexpected: unhealthyDevices and endpoints are out of sync")
}
delete(m.endpoints, resourceName)
delete(m.unhealthyDevices, resourceName)
deletedResources.Insert(resourceName)
needsUpdateCheckpoint = true
} else {
capacityCount := capacity[v1.ResourceName(resourceName)]
unhealthyCount := *resource.NewQuantity(int64(devices.Len()), resource.DecimalSI)
capacityCount.Add(unhealthyCount)
capacity[v1.ResourceName(resourceName)] = capacityCount
}
}
m.mutex.Unlock()
if needsUpdateCheckpoint {
if err := m.writeCheckpoint(); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("writing checkpoint encountered %v", err)
}
}
return capacity, allocatable, deletedResources.UnsortedList()
}
GetCapacity会遍历所有的Device,统计每种资源的:
capacity:总资源量allocatable:健康的资源量deletedResources:删除的资源
Kubelet对GetCapacity的调用
我们刚刚看到了统计资源总量的GetCapacity函数,接下来我们看调用它的containerManagerImpl.GetDevicePluginResourceCapacity函数。
func (cm *containerManagerImpl) GetDevicePluginResourceCapacity() (v1.ResourceList, v1.ResourceList, []string) {
return cm.deviceManager.GetCapacity()
}
在pkg/kubelet/nodestatus/setters.go中的MachineInfo中:
......
......
......
devicePluginCapacity, devicePluginAllocatable, removedDevicePlugins = devicePluginResourceCapacityFunc()
for k, v := range devicePluginCapacity {
if old, ok := node.Status.Capacity[k]; !ok || old.Value() != v.Value() {
klog.V(2).InfoS("Updated capacity for device plugin", "plugin", k, "capacity", v.Value())
}
node.Status.Capacity[k] = v
}
for _, removedResource := range removedDevicePlugins {
klog.V(2).InfoS("Set capacity for removed resource to 0 on device removal", "device", removedResource)
node.Status.Capacity[v1.ResourceName(removedResource)] = *resource.NewQuantity(int64(0), resource.DecimalSI)
}
......
......
......
for k, v := range devicePluginAllocatable {
if old, ok := node.Status.Allocatable[k]; !ok || old.Value() != v.Value() {
klog.V(2).InfoS("Updated allocatable", "device", k, "allocatable", v.Value())
}
node.Status.Allocatable[k] = v
}
这里会对Capacity、Allocatable资源列表进行拷贝,并且遍历GetDevicePluginResourceCapacity返回已超时需要删除的资源,在总资源列表中将这些资源的数量置为0(之所以置为0,是用于区别,设备插件托管资源和节点状态中不存在的集群级资源)这句话我没看懂,机翻的
Scheduler对资源的管理
kubernetes/pkg/scheduler/framework/types.go
type Resource struct {
MilliCPU int64
Memory int64
EphemeralStorage int64
AllowedPodNumber int
ScalarResources map[v1.ResourceName]int64
}
资源添加
可以看到:k8s默认管理四种固有资源:CPU、内存、存储,Pod。除此之外,还有我们关注的扩展资源ScalarResources,Resource记录了这些资源的数量。同时,设置了一些方法来管理资源:
// Add adds ResourceList into Resource.
func (r *Resource) Add(rl v1.ResourceList) {
if r == nil {
return
}
for rName, rQuant := range rl {
switch rName {
case v1.ResourceCPU:
r.MilliCPU += rQuant.MilliValue()
case v1.ResourceMemory:
r.Memory += rQuant.Value()
case v1.ResourcePods:
r.AllowedPodNumber += int(rQuant.Value())
case v1.ResourceEphemeralStorage:
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.LocalStorageCapacityIsolation) {
// if the local storage capacity isolation feature gate is disabled, pods request 0 disk.
r.EphemeralStorage += rQuant.Value()
}
default:
if schedutil.IsScalarResourceName(rName) {
r.AddScalar(rName, rQuant.Value())
}
}
}
}
// AddScalar adds a resource by a scalar value of this resource.
func (r *Resource) AddScalar(name v1.ResourceName, quantity int64) {
r.SetScalar(name, r.ScalarResources[name]+quantity)
}
// SetScalar sets a resource by a scalar value of this resource.
func (r *Resource) SetScalar(name v1.ResourceName, quantity int64) {
// Lazily allocate scalar resource map.
if r.ScalarResources == nil {
r.ScalarResources = map[v1.ResourceName]int64{}
}
r.ScalarResources[name] = quantity
}
这里设置了Add方法,将一个Node中的所有资源(v1.ResourceList)添加到Scheduler中进行管理。
资源申请的预验证
在向Scheduler申请资源时,会调用Fits方法,如下:
// Fits checks if node have enough resources to host the pod.
func Fits(pod *v1.Pod, nodeInfo *framework.NodeInfo) []InsufficientResource {
return fitsRequest(computePodResourceRequest(pod), nodeInfo, nil, nil)
}
// preFilterState computed at PreFilter and used at Filter.
type preFilterState struct {
framework.Resource
}
func fitsRequest(podRequest *preFilterState, nodeInfo *framework.NodeInfo, ignoredExtendedResources, ignoredResourceGroups sets.String) []InsufficientResource {
insufficientResources := make([]InsufficientResource, 0, 4)
allowedPodNumber := nodeInfo.Allocatable.AllowedPodNumber
if len(nodeInfo.Pods)+1 > allowedPodNumber {
insufficientResources = append(insufficientResources, InsufficientResource{
v1.ResourcePods,
"Too many pods",
1,
int64(len(nodeInfo.Pods)),
int64(allowedPodNumber),
})
}
if podRequest.MilliCPU == 0 &&
podRequest.Memory == 0 &&
podRequest.EphemeralStorage == 0 &&
len(podRequest.ScalarResources) == 0 {
return insufficientResources
}
if podRequest.MilliCPU > (nodeInfo.Allocatable.MilliCPU - nodeInfo.Requested.MilliCPU) {
insufficientResources = append(insufficientResources, InsufficientResource{
v1.ResourceCPU,
"Insufficient cpu",
podRequest.MilliCPU,
nodeInfo.Requested.MilliCPU,
nodeInfo.Allocatable.MilliCPU,
})
}
if podRequest.Memory > (nodeInfo.Allocatable.Memory - nodeInfo.Requested.Memory) {
insufficientResources = append(insufficientResources, InsufficientResource{
v1.ResourceMemory,
"Insufficient memory",
podRequest.Memory,
nodeInfo.Requested.Memory,
nodeInfo.Allocatable.Memory,
})
}
if podRequest.EphemeralStorage > (nodeInfo.Allocatable.EphemeralStorage - nodeInfo.Requested.EphemeralStorage) {
insufficientResources = append(insufficientResources, InsufficientResource{
v1.ResourceEphemeralStorage,
"Insufficient ephemeral-storage",
podRequest.EphemeralStorage,
nodeInfo.Requested.EphemeralStorage,
nodeInfo.Allocatable.EphemeralStorage,
})
}
for rName, rQuant := range podRequest.ScalarResources {
if v1helper.IsExtendedResourceName(rName) {
// If this resource is one of the extended resources that should be ignored, we will skip checking it.
// rName is guaranteed to have a slash due to API validation.
var rNamePrefix string
if ignoredResourceGroups.Len() > 0 {
rNamePrefix = strings.Split(string(rName), "/")[0]
}
if ignoredExtendedResources.Has(string(rName)) || ignoredResourceGroups.Has(rNamePrefix) {
continue
}
}
if rQuant > (nodeInfo.Allocatable.ScalarResources[rName] - nodeInfo.Requested.ScalarResources[rName]) {
insufficientResources = append(insufficientResources, InsufficientResource{
rName,
fmt.Sprintf("Insufficient %v", rName),
podRequest.ScalarResources[rName],
nodeInfo.Requested.ScalarResources[rName],
nodeInfo.Allocatable.ScalarResources[rName],
})
}
}
return insufficientResources
}
这段代码的意思非常简单:检查所有资源类型,如果对于当前的资源类型,如果有:
$$
Allocatable - Requested > podRequest
$$
那么将该资源的请求数量、已使用数量、总数信息塞到insufficientResources中返回。
总结
通过今天的学习,发现:
- k8s中,管理着三种固有资源:CPU、内存、存储,以及一种虚拟资源Pod,还可以支持外部资源
- k8s中资源的管理是逐层递进的:
Master–>Node–>Device,资源的管理与统计是逐层向上汇总的 - 对资源管理的过程实质上就是对所需的不同类型资源的剩余进行统计的过程
想要实现一个自定义资源,只需要实现资源的Register、ListAndListen、Allocated三种方法即可,因为当一个资源拥有了这三种方法后,就可以完成Device到Node的资源的增删改查。这一过程,实质上就是Device Plugin和Kubelet通信的过程。